Principal Investigator

Staff
Research topic
Grasping the molecular basis of cell adhesion dynamics to design effective “vascular normalizing” drugs for cancer therapy.
Background
Tumor blood vessels are structurally and functionally abnormal, which hinders the delivery of anticancer drugs and prevents immune cells from entering the cancerous tissue. Furthermore, hypoxia caused by vascular abnormalities promotes genetic instability and the selection of aggressive tumor cell clones, as well as metastatic dissemination. Therefore, normalization of tumor vasculature holds great promise as a strategy to sizably improve anticancer therapy. The binding of vascular endothelial cells (ECs) to the extracellular matrix (ECM) is mediated by integrins, a class of adhesive receptors that can assume active or inactive conformations, respectively characterized by high or low binding affinity to ECM ligands. Blood fluid shear stress is the main determinant of normal vascular architecture and function, driving the activation of integrins and promoting EC-to-ECM adhesion. As a direct consequence, ECs modify their adhesive interactions, eventually resulting in a remodeled, mature and functional vascular tree. In this framework, inhibitors of integrin function may ensure rapid responsiveness of EC-ECM adhesion to changes induced by blood flow. Therefore, pharmacological modulation of integrin function could be therapeutically exploited to “normalize” the tumor vasculature.
Research results
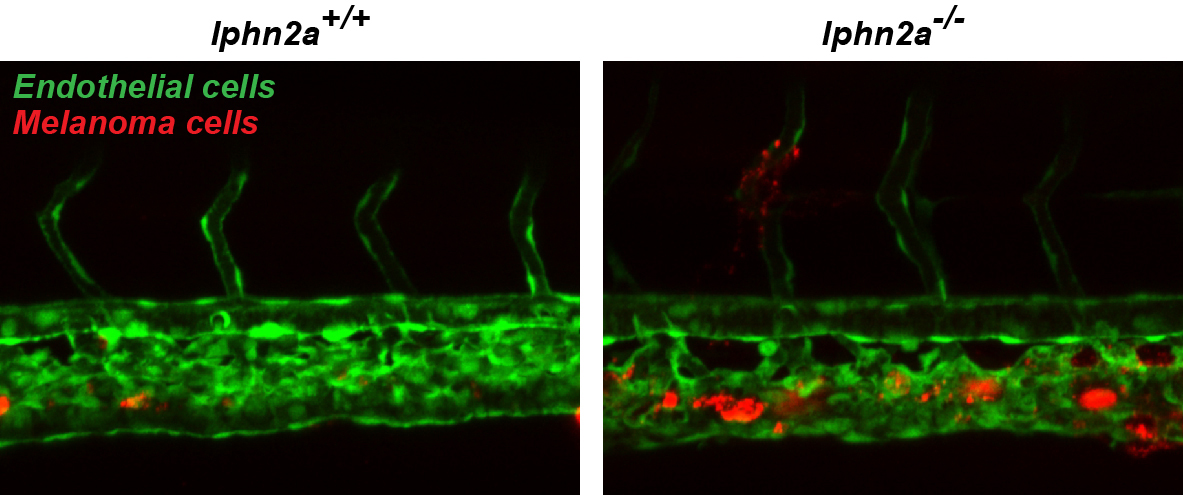
Previously, we showed that the loss of integrin-dependent inhibitory signals triggered by chemorepulsive semaphorin 3A (SEMA3A), via plexin and neuropilin-1 (NRP1) receptors, underpins the abnormalities that hallmark tumor blood vessels. In collaboration with the Tumor Microenvironment Laboratory at our Institute, we then generated a mutant SEMA3A protein (Mut-SEMA3A) that can be administered parenterally. Due to its ability to bind with high affinity the plexin A4 signaling receptor, Mut-SEMA3A, by physiologically inhibiting small GTPase RAP1-mediated activation of endothelial integrins, normalizes cancer vascular abnormalities, enhances penetration of antineoplastic drugs, and counteracts metastasis. Next, we established that the chemorepulsive fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein 2 (FLRT2) ligand, through its receptor latrophilin 2 (LPHN2), prevents the RAP1-dependent activation of vascular endothelial integrins and counteracts the extravasation of circulating cancer cells. We also revealed how, upon its unconventional secretion, the splicing variant of tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase (mini-WARS) acts as an extracellular inhibitory ligand of NRP1, slowing down the endocytic turnover of intercellular adhesive receptors and counteracting endothelial leakage. More recently, we prototyped a luminescent integrin β1 sensor that enabled us to identify, in high-content screenings, new physiological inhibitors of its conformational activation in ECs that could be targeted pharmacologically to normalize tumor vasculature, such as VEGF-B.
Conclusions and perspectives
Our data provide strength to the hypothesis that negative pharmacological modulation of endothelial integrins by different signaling pathways can be exploited therapeutically to enhance the biodistribution of antineoplastic drugs and counteract the extravasation and metastatic dissemination of cancer cells. Therefore, it will be key to: i) identify novel mechanisms and molecular determinants responsible for inhibiting the activation of different integrins in ECs; ii) test the pharmacological exploitability of the novel vasculature normalizing factors that we have identified (e.g., FLRT2, mini-WARS, and VEGF-B) and will identify.
Publications
At this link, you can find all the scientific publications of the Principal Investigator.
Selected publications
G. Villari, N. Gioelli, M. Gino, H. Zhang, K. Hodge, F. Cordero, S. Zanivan, J. Zhu, G. Serini. Luminescent sensing of conformational integrin activation in living cells. Cell Rep., 2025, 44(2):115319.
N. Gioelli, L.J. Neilson, N. Wei, G. Villari, W. Chen, B. Kuhle, M. Ehling, F. Maione, S. Willox, S. Brundu, D. Avanzato, G. Koulouras, M. Mazzone, E. Giraudo, X.L. Yang, D. Valdembri, S. Zanivan, G. Serini. Nat. Commun., 2022, 13:4188.
C. Camillo*, N. Facchinello*, G. Villari*, G. Mana, N. Gioelli, C. Sandri, M. Astone, D. Tortarolo, F. Clapero, D. Gays, R.E. Oberkersch, M. Arese, L. Tamagnone, D. Valdembri, M.M. Santoro, G. Serini. LPHN2 inhibits vascular permeability by differential control of endothelial cell adhesion. J. Cell Biol., 2021, 220(11):e202006033. Shared *first authorship.
G. Villari, C. Enrico Bena, M. Del Giudice, N. Gioelli, C. Sandri, C. Camillo, A. Fiorio Pla, C. Bosia, and G. Serini. EMBO J. 2020, 39:e103661.
N. Gioelli*, F. Maione*, C. Camillo, M. Ghitti, D. Valdembri, N. Morello, M. Darche, L. Zentilin, G. Cagnoni, Y. Qiu, M. Giacca, M. Giustetto, M. Paques, I. Cascone, G. Musco, L. Tamagnone#, E. Giraudo#, G. Serini#. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10: eaah4807. Shared *first/#last authorship.